EBUS?
What is EBUS?
Endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) is a minimally invasive but highly effective procedure used to diagnose lung cancer, infections, and other diseases causing enlarged lymph nodes in the chest. Dr Sameer Arbat is the first doctor to have Central India’s first and only EBUS & Cryobiopsy Unit.
Why is EBUS used?
EBUS allows physicians to perform a technique known as transbronchial needle aspiration (TBNA) to obtain tissue or fluid samples from the lungs and surrounding lymph nodes without conventional surgery. The samples can be used for diagnosing and staging lung cancer, detecting infections, and identifying inflammatory diseases that affect the lungs, such as sarcoidosis or cancers like lymphoma.
What makes EBUS different?
During a conventional diagnostic procedure, surgery known as mediastinoscopy is performed to provide access to the chest. It involves giving an incision in the chest and carries some risks and complications.
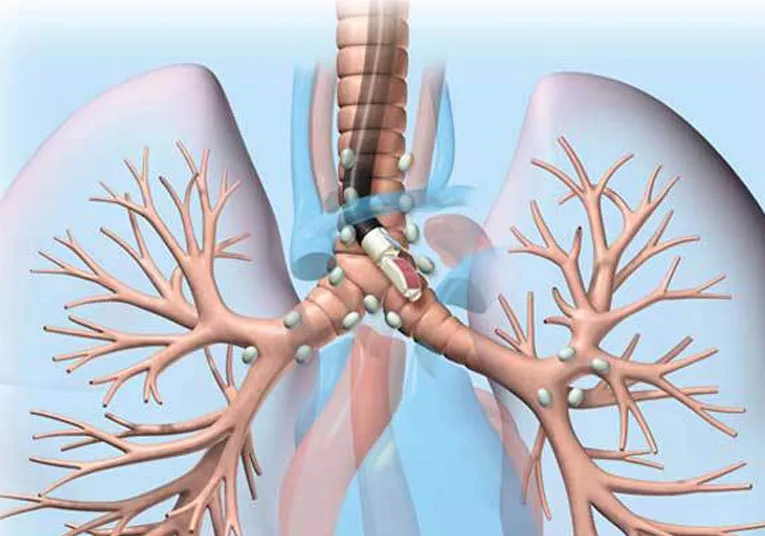
An endobronchial ultrasound is much less invasive. The physician can perform needle aspiration on lymph nodes using a bronchoscope inserted through the mouth. A special endoscope fitted with an ultrasound processor and a fine-gauge aspiration needle is guided through the patient’s trachea. No incisions are necessary.
What are the Benefits of EBUS?
It provides real-time imaging of the surface of the airways, blood vessels, lungs, and lymph nodes. The improved images allow the physician to easily view difficult-to-reach areas and to access more, and smaller, lymph nodes for biopsy with the aspiration needle than through conventional mediastinoscopy.
The accuracy and speed of the EBUS procedure lend themselves to rapid onsite pathologic evaluation. Pathologists in the operating room can process and examine biopsy samples as they are obtained and can request additional samples to be taken immediately if needed. EBUS is performed under moderate sedation or general anaesthesia. Patients recover quickly and can usually go home the same day.